Jalapeños and Fresnos are two popular chili peppers that have become staples in many kitchens. Known for their vibrant flavors and moderate heat, these peppers add a delightful kick to a wide range of dishes. But you may think what is there to know when comparing jalapeño vs Fresno chili peppers?
Jalapeño vs Fresno Chili Peppers
Whether you’re a fan of Mexican cuisine or simply enjoy adding a touch of spice to your meals, jalapeños and Fresnos are versatile ingredients that can elevate your culinary creations.
Jalapeños, with their bright green color and distinctive heat, are widely recognized as one of the most popular chili peppers. They offer a pleasant balance between spiciness and flavor, making them suitable for a variety of dishes.
On the other hand, Fresnos bring a similar level of heat but with a unique flavor profile. Their vibrant red color and fruity undertones make them a favorite among chili enthusiasts. In this post, we’ll explore the characteristics, culinary uses, and key differences of jalapeños and Fresnos, providing you with insights to enhance your cooking.
Origins of the Jalapeño
The jalapeño pepper, scientifically known as Capsicum annuum, is believed to have originated in Mexico. Mexico is considered the primary birthplace of many chili pepper varieties due to its rich culinary history and diverse ecosystems. Within Mexico, the city of Xalapa (also spelled Jalapa) in the state of Veracruz is often associated with the origin of the jalapeño pepper.
Veracruz, located in eastern Mexico along the Gulf of Mexico, has a favorable climate for pepper cultivation. It is known for its fertile soil, abundant rainfall, and moderate temperatures, which provide optimal conditions for pepper plants to thrive. The region’s agricultural heritage and long tradition of chili pepper cultivation contribute to the belief that the jalapeño pepper originated in this area.
These green peppers have been a staple ingredient in Mexican cuisine for centuries. Its distinct flavor and moderate heat level make it a versatile chili pepper used in a wide range of dishes. From traditional salsas and guacamole to tacos, enchiladas, and more, the Jalapeño pepper adds a zesty and slightly spicy kick to various Mexican dishes. Its popularity and widespread cultivation have led to its introduction and adoption in cuisines around the world.
Origins of the Fresno
The Fresno chile, also a variety of Capsicum annuum, is very similar to the jalapeño pepper. It is specifically associated with the city of Fresno in California, being named after the city due to its popularity and the region’s significant role in its commercial cultivation and distribution.
However, it’s important to note that the Fresno chile did not originate in Fresno itself but rather found its way to the region through cultivation and commercialization. The first commercial cultivation of these red Fresno peppers is often attributed to the late Clarence Brown Hamlin, a farmer from Fresno, California, who grew them in the San Joaquin Valley.
In the early 1950s, Hamlin started growing and selling a particular variety of chili pepper that eventually became known as the Fresno chile. He recognized its potential as a marketable crop due to its vibrant red color, mild to moderate heat level, and versatility in culinary applications.
With the rise of Mexican and Southwestern cuisines’ popularity in the United States, the Fresno chile gained traction and became a sought-after ingredient, particularly in the Central Valley region of California. Its commercial cultivation expanded, and it became widely available in local markets and grocery stores.
The Fresno’s popularity continues to grow, and it is now used in various dishes, including salsas, sauces, marinades, and as a flavorful addition to many recipes where a mild to moderate heat level is desired.
Jalapeño Appearance
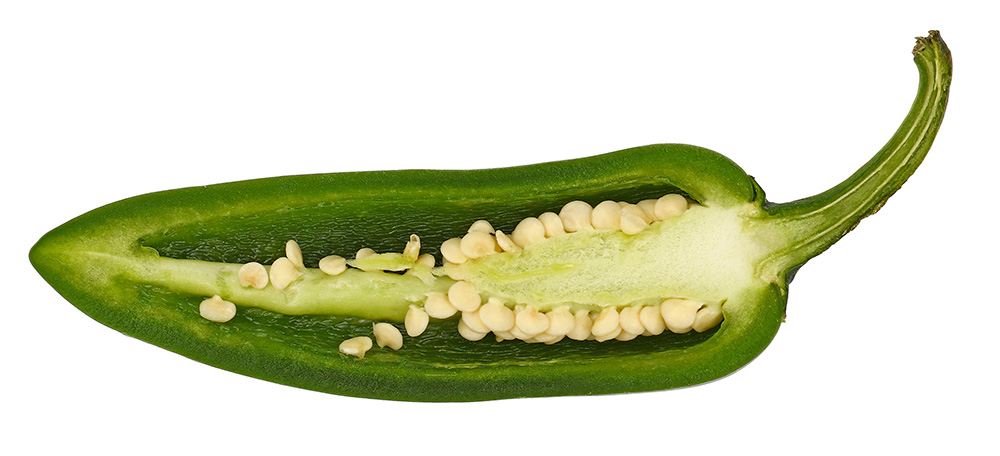

The jalapeño pepper typically measures around 2 to 3 inches in length and has a slightly curved shape, resembling a small elongated cone. Its skin is smooth and shiny, ranging in color from bright green when young to a deeper, darker green as it matures. However, as the jalapeño ripens further, it can turn into shades of red. The red jalapeno, though, is far less common in the grocery store.
Along the pepper’s surface, you may notice faint lines or creases that run from the stem to the tip. These lines add texture to its appearance. Inside, the jalapeño contains a cavity filled with small, white to pale yellow seeds.
Fresno Appearance
The Fresno pepper shares some similarities in appearance with the jalapeño pepper. It is generally medium-sized, ranging from 2 to 3 inches in length. It has a slightly curved shape, tapering towards the tip.
When young, the Fresno pepper starts off green and transitions to a bright red color as it matures. The skin of the pepper is smooth and glossy, giving it an attractive and inviting appearance. Inside the pepper’s thin walls, you’ll find a central cavity filled with small, pale-colored seeds.
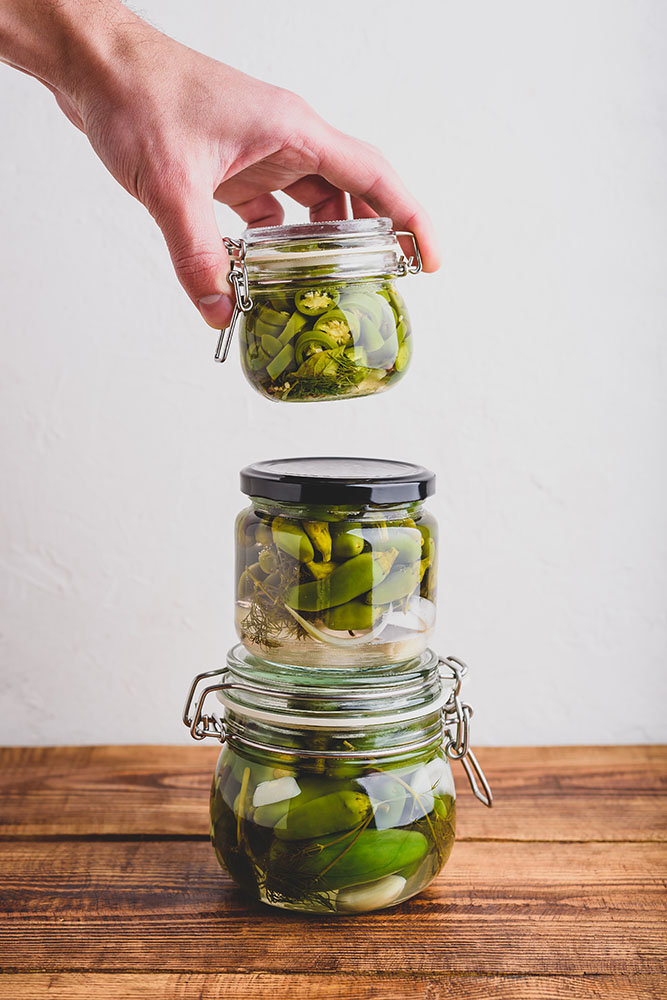

Jalapeño Culinary Uses
Jalapeños are widely used in cooking for their spicy flavor and versatility. They are commonly added to salsas, dips, and spicy condiments to enhance the taste. These peppers can be found in various cuisines, including Mexican and Southwestern dishes. They are often used as toppings, garnishes, or stuffed with fillings for appetizers.
Jalapeños can also be pickled or used to infuse oils and vinegars, adding a spicy kick to dressings, marinades, and sauces. They are also commonly smoked and dried, which are then called chipotle peppers. With their distinct taste, jalapeños are an excellent choice for those seeking to add some heat to their meals.
Fresno Culinary Uses
The Fresno pepper is a versatile chili pepper known for its moderate heat and fruity flavor. It is often used in salsas, hot sauces, and marinades to add a tangy, spicy kick. Its medium heat level makes it suitable for those who enjoy a bit of heat without overpowering their taste buds.
The Fresno pepper can be used fresh, dried, or roasted, offering different flavor profiles and intensities. Its vibrant red color also makes it visually appealing when used as a garnish or ingredient in dishes.
Scoville Scale Facts
Scoville units are a measurement scale used to quantify the heat or spiciness of chili peppers and other spicy foods. The scale is named after pharmacist Wilbur Scoville, who developed it in 1912. It assigns a numerical value to peppers based on the amount of capsaicin, the chemical compound responsible for the sensation of heat, which ranges from 0 (bell peppers) to 2,000,000+ (Carolina Reaper).
Jalapeño peppers typically have a Scoville rating ranging from 2,500 to 8,000 units, making them moderately spicy. In comparison, Fresno peppers have a slightly higher Scoville rating, ranging from 2,500 to 10,000 units.
While both peppers offer a noticeable kick of heat, they are generally considered milder in comparison to extremely hot peppers like the Carolina Reaper, which can exceed two million Scoville units.
Jalapeño vs Fresno Chili Peppers: How Do They Compare?
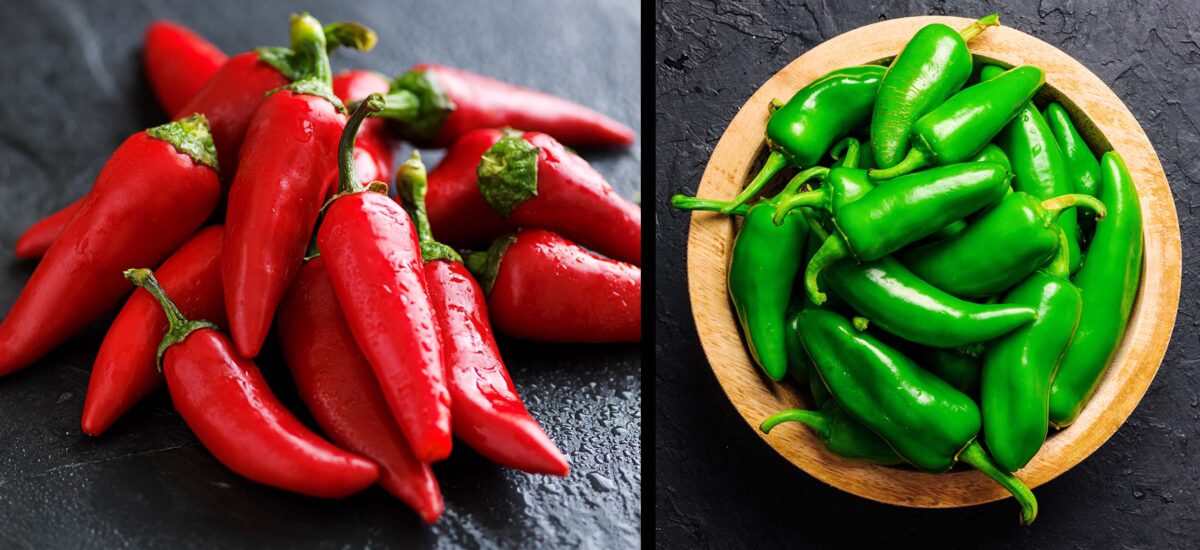
Jalapeños and Fresnos are both popular chili peppers, but they have some key differences. In terms of appearance, jalapeños are typically shorter and wider, with a smooth and shiny dark green skin with thick walls that turn red when fully ripe. On the other hand, Fresnos have thinner walls and are slightly longer and narrower, with a similar green color that matures to a vibrant red or orange.
When it comes to flavor, jalapeños have a distinctive balance of heat and tanginess. They offer a moderate level of spiciness, with a Scoville rating ranging from 2,500 to 8,000 units. Jalapeños are often described as having a crisp, grassy flavor with a hint of sweetness. They are commonly used in a wide range of dishes, such as salsas, guacamole, and stuffed jalapeño poppers.
Fresno peppers, on the other hand, have a similar heat profile to jalapeños, ranging from 2,500 to 10,000 Scoville units. However, Fresnos tend to be slightly hotter and fruitier in taste. They can have a somewhat smoky flavor, with hints of berry and citrus. Fresnos can be used in various culinary applications, including sauces, marinades, and as a versatile ingredient in Mexican and Southwestern cuisine.
Overall, while both jalapeños and Fresnos offer a pleasant level of spiciness, Fresnos tend to have a slightly hotter and fruitier taste compared to jalapeños. The choice between the two can depend on personal preference and the specific flavor desired for a particular dish.
Other notable chiles
Serrano Pepper
Serrano peppers are moderately hot chili peppers with a Scoville rating ranging from 10,000 to 23,000 units. They have a bright and crisp flavor with a higher level of heat compared to jalapeno peppers. Serrano peppers are commonly used in salsas, marinades, and spicy Mexican dishes, providing a spicy kick without being overly overpowering, which make them the best substitutes for jalapeños and Fresnos.
Habanero Pepper
Known for its intense heat, the habanero pepper is one of the hottest chili peppers commonly used in culinary applications. It ranges from 100,000 to 350,000 Scoville units, making it significantly hotter than jalapeños and Fresnos. Habanero peppers have a fruity and citrusy flavor, adding a fiery kick to dishes like salsas, hot sauces, and spicy marinades.
Scotch Bonnet Pepper
Similar in heat level and flavor to the habanero, the Scotch bonnet pepper is a staple in Caribbean cuisine. It shares the same range of Scoville units, delivering a fiery and fruity taste. Scotch bonnets are often used in jerk seasoning, Caribbean stews, and spicy condiments.
Cayenne Pepper
Cayenne peppers are known for their fiery heat and bold flavor, making them a popular ingredient in many cuisines. These slender, elongated peppers have a vibrant red color and pack a punch with Scoville heat units ranging from 30,000 to 50,000. With their distinctive earthy and slightly sweet taste, cayenne peppers add a spicy kick to dishes.
Ghost Pepper (Bhut Jolokia)
Ghost peppers held the title of the world’s hottest pepper for a time, with a Scoville rating of over 1 million units. They have a powerful, lingering heat that can be overwhelming for some. Ghost peppers are commonly used in sauces, salsas, and spicy snacks, but should be approached with caution due to their extreme spiciness.
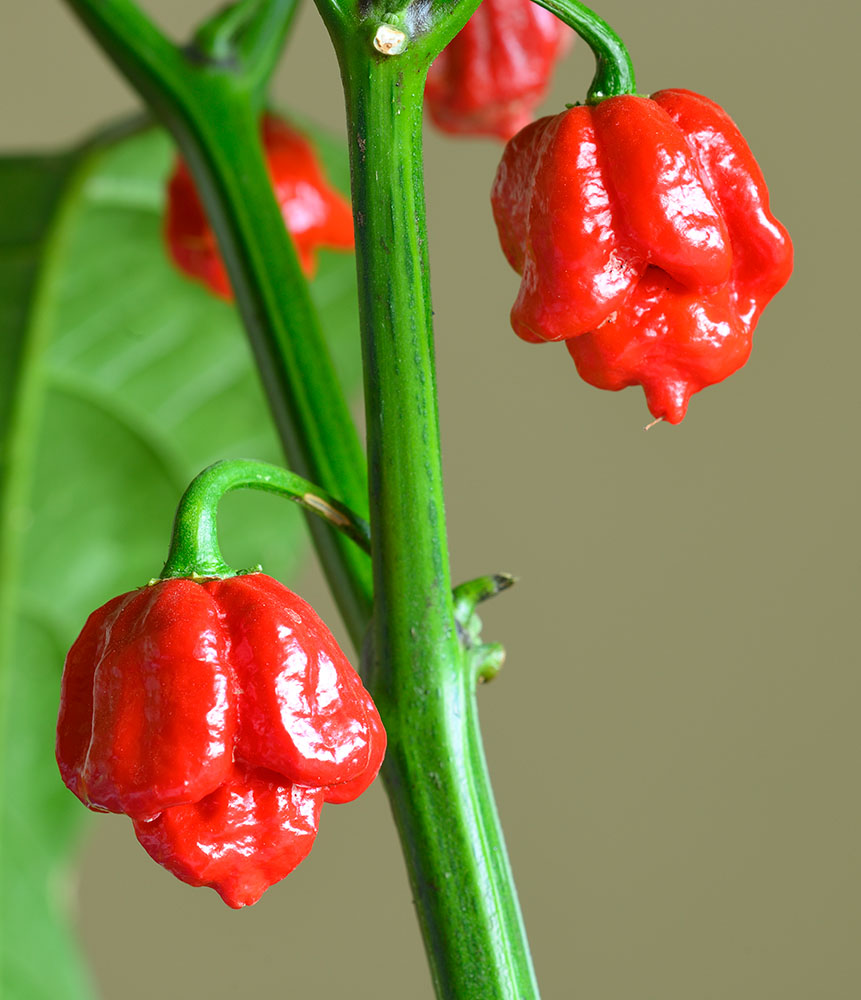

Carolina Reaper
Currently holding the Guinness World Record as the hottest chili pepper, the Carolina Reaper measures over 1.5 million Scoville units. This pepper has a fruity and sweet flavor initially, followed by an intense and prolonged heat. The Carolina Reaper is primarily used in small quantities to add extreme heat to dishes, such as hot sauces, chili, and spicy marinades.
Anaheim Pepper
The Anaheim pepper is a mild chili pepper with a Scoville rating ranging from 500 to 2,500 units. It has a thin skin and a slightly sweet flavor with a touch of spiciness. Anaheim peppers are commonly used in Mexican and Southwestern cuisine, often roasted and added to dishes like salsas, sauces, and stuffed peppers.
Banana Pepper
Banana peppers are mild chili peppers with a Scoville rating typically between 0 and 500 units. They have a mild and tangy flavor, resembling the taste of a sweet banana. Banana peppers are often pickled and used in salads, sandwiches, and as a topping for pizzas and burgers.
These peppers offer a range of heat levels and flavors, allowing for various culinary applications. Whether you’re looking for mild and tangy flavors or a moderate level of spiciness, these peppers can add a delightful kick to your dishes. As with any chili pepper, it’s always a good idea to handle them with care and be mindful of their heat level when incorporating them into your recipes.





2 thoughts on “Jalapeño vs Fresno Chili Peppers: What’s to Know?”